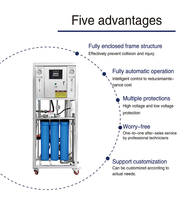
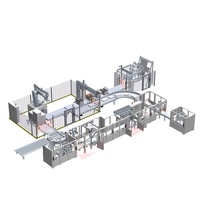
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
mineral water plant
Types of mineral water plants
Any natural water source can be turned into a spring water or mineral water plant, but only a few qualified geological features can genuinely yield water of mineral quality that fits the acceptable standards. The majority of the wells or springs connected to mineral water plants are located in secluded rural regions. These are deep subterranean aquifers with a special geological anatomy, such as cracks in limestone bedrock that permit the water to come in direct contact with rock, allowing dissolved minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium to give the water a specific geological taste and odor.
Deep wells, springs, and boreholes representative of proper geological settings are the sources of mineral water plants. Their locations are crucial to the water's flavor, odor, and mineral composition. Before setting up a mineral water plant, having proper knowledge of the geology, terrain, and hydrology will aid in guaranteeing a constant supply of water and the quality of the finished product. Only after thorough investigation and analysis can the site's suitability for the mineral water plant be determined. The area will be devoted to extracting and processing mineral-rich water for human consumption.
Due to the significance of maintaining quality control throughout the process of mineral water extraction, processing, bottling, and distribution, personnel training is equally as important as technology. The main characteristics of any mineral water plant are as follows:
- Spring Water Plant:It is located close to natural springs. They gather and process spring water after ensuring it is free of pollutants and impurities. The water comes directly from the earth with little to no treatment. Because it comes from a deeper layer of the earth and typically passes through mineral-rich rocks, spring water has a distinctive mineral composition and taste.
- Deep Well Water Plant:These extract water from deep underground aquifers. Unlike surface water, which can be easily contaminated, deep well water is located much below the surface. The water is typically pure and requires some basic treatment and filtration to make it safe for human consumption.
- Purified Water Plant:These plants process water that has been heavily filtered and treated to remove all contaminants, including dissolved solids like minerals. Even though it resembles mineral water, the flavor and characteristics are fundamentally different. Reverse osmosis is the water purification method used in these plants. The final product is pure H2O with few or no dissolved minerals.
Specifications and Maintenance
Specifications
The specifications of a mineral water manufacturing plant may vary depending on the individual needs, capacity, and available technology.
-
Capacity:
It is usually described in liters per hour or bottles per hour. For example, a small mineral water plant could have a capacity of 500 to 2,000 liters per day, while large commercial plants produce 10,000 to 50,000 liters per day or more.
-
Production Line Components:
A mineral water plant may include many components, such as water source supply systems, water treatment systems (pre-filtration, reverse osmosis, UV sterilization, etc.), bottling systems, sealing systems, labeling systems, packaging systems, etc.
-
Power:
Some small plants may use mains electricity or solar power. Others may be connected to industrial power grids and use electric or gas power as an energy source.
-
Plant Area:
The area occupied by the mineral water plant depends on the facilities' scale and capacity. A small plant could occupy an area of 100 to 500 square meters, while large plants could occupy an area of several thousand square meters.
Maintenance
-
Clean:
Clean the equipment and production line of the mineral water plant thoroughly. Use appropriate cleaning agents and techniques to ensure no residual contaminants. Also, develop a regular cleaning schedule to ensure long-term compliance with hygienic standards.
-
Quality Maintenance:
Carry out quality maintenance for key components and equipment of the mineral water plant, including filtering membranes, UV lamps, water pumps, bottling heads, etc. Replace parts that are damaged or worn out and keep the equipment operating smoothly.
-
Calibrate and Adjust:
Regularly calibrate and adjust the parameters of the water treatment system and bottling system to ensure the proper functioning of the equipment and the stability of the product quality.
Uses of mineral water plant
Mineral water plants aren't just used for large-scale bottling operations anymore. Thanks to the versatility of the plants and the growing demand for pure drinking water across the globe, several sectors now use these plants to produce mineral water.
- Beverage industry: The beverage industry is perhaps the main user of mineral water plants. Beverages such as soft drinks, energy drinks, fruit concentrates, and even whiskies require high-quality water as an ingredient. Some plants even have water treatment systems that assist in eliminating contaminants and enhancing the taste of the water, which is then used as an ingredient in these beverages. By incorporating water treatment plants into their production processes, beverage manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the highest quality standards and are free from impurities that could affect the taste or safety of the final product.
- Hospitality industry: The hospitality industry, particularly hotels, restaurant chains, and cafes, are also huge users of mineral water plants. Many hotels offer their guests branded hotel mineral water. Some even allow guests to infuse their water bottles with fruits and herbs of their choice. With the increasing popularity of locally sourced and sustainable products, many hotels and restaurants are opting for on-site water bottling as a way to reduce their carbon footprint and provide their customers with a unique offering.
- Fitness and health industry: Gyms and spas often use small-scale mineral water bottling plants. These fitness centers usually offer their customers cold-pressed juices and mineral water. Some even offer flavored mineral water to attract more customers. With the rising awareness of the importance of hydration and the preference for natural and chemical-free products, flavored mineral water has gained immense popularity among health-conscious consumers. Fitness centers and gyms are prime distributors of these products, catering to individuals who prioritize their health and well-being. By offering flavored mineral water as an alternative to sugary drinks, fitness centers and gyms not only provide a refreshing and healthy option but also promote the importance of staying hydrated for optimal physical performance and overall wellness.
- Retail: Convenience stores, supermarkets, and vending machine owners also use mineral water plants to produce flavored and unflavored water. The bottled water is then stocked and sold at retail outlets for consumers' convenience. The proliferation of convenient retail outlets that sell bottled mineral water has made it a staple product for busy individuals on the go.
- Agriculture: Agriculture is also a surprising industry that uses mineral water plants. High-value crops that require pure water for irrigation utilize these water plants to produce mineral water for irrigation. Irrigation with mineral water can alleviate soil salinity and improve crop productivity, making it a valuable tool for farmers aiming to maximize their yields and maintain the quality of their produce.
How to choose a mineral water plant
Here are some essential tips when choosing a mineral water bottle making plant:
- Quality of water sources: Assess the quality of water sources near the business location. If the location relies on borehole or tap water, consider investing in effective treatment plants.
- Capacity: Estimate the desired production capacity based on market demand, business goals, and potential for expansion. Consider a plant with adaptable components to meet changing capacity needs.
- Filtration system: Choose an advanced filtration system, like reverse osmosis (RO), which can remove impurities, minerals, and contaminants, to ensure excellent water quality.
- Industry standards and certifications: The equipment used in the mineral water production plant should comply with industry standards and possess essential certifications. Choose suppliers that can show their compliance documentation and certification.
- Space requirements: Know the mineral water plants' space requirements to ensure sufficient room for the safe and effective installation, operation, and future expansion in the given business location.
- Maintenance and support: Choose a supplier that offers excellent maintenance and support services. Check their nationwide service network, spare part availability, and technical support throughout the plant's life cycle.
- Cost: Consider the overall cost, including purchase pricing, operating expenses, and potential for energy efficiency. Take at least a 5-year running cost into account when comparing different plants.
- Energy efficiency: Choose an efficient mineral water plant to reduce business operating costs and environmental impact.
- Scalability: Opt for a plant with special treatment and bottling lines that can scale up the production capacity as the market demand increases.
- Technological advancements: Pay attention to the latest technological developments in mineral water plants, such as automated bottling lines, efficient filtration systems, and advanced quality control methods.
- Environmental considerations: Choose a plant that adopts energy-saving treatment methods and uses recyclable bottles to reduce mineral resource depletion and environmental pollution.
Q&A
Q1: What is the procedure in a mineral water plant?
A1: Source water analysis is done at the start of the procedure. After that, the water is prefelted, followed by carbon dioxide removal. The next steps include reverse osmosis, mineral addition, final filtration, bottling, and packaging.
Q2: How much electricity does a mineral water plant consume?
A2: One mineral water plant consumes approximately 9,000 units of electricity each month.
Q3: How much land is required to set up a mineral water plant?
A3: One mineral water plant requires at least 0.2 acres of land.
Q4: What is the initial investment cost of a mineral water plant?
A4: The initial investment cost of a small to mid-sized mineral water plant is between 50,000 to 1 million US dollars.
Q5: What are the latest technologies used in mineral water plants?
A5: The latest technology used in mineral water plants is airless, ozone-free, and pressurized water filtration.